# Roomle Script Language Reference
This document provides a reference for the RoomleScript language, which is contained in the values of the Roomle Component Definition JSON objects and is a proprietary language for scripts interpreted by the Rubens Configurator core.
RoomleScript's syntax is loosely based on the JavaScript language and provides extensive possibilities to use in the component definitions.
# Variables
Variables are declared automatically without any keywords. Type is also assigned automatically and there is no type declaration. To undeclare/delete a variable, which is not a parameter, you can use the setnull function. Functions ifnull and isnull can be checked if a variable is declared.
WARNING If a variable is accessed before the declaration, it will be interpreted as a String.
Variables can also be declared in the connection, other and other_connection contexts.
Parameters and superseded parameters are accessible by their key attribute in the same way as a variable.
The scope of variables is different for different scripts. See Scopes for details.
Example:
- Declare a variable:
width = 500; /* width is declared and initialized to value 500 */
- Undeclare a variable:
setnull(width); /* width is deleted */
if (isnull(width)) {
/* isnull is true after width has been set to null */
/* do something */
}
- Check if components on both sides of the connection have a width declared and store information about it in this component:
self.widthDeclaredOnBothSides = !isnull(self.width) && !isnull(other.width);
- Store indices
iandjin the current connection (i.e. in a docking point of a docking range):
connection.i = xFromVector(connection.position) / 200;
connection.j = zFromVector(connection.position) / 200;
- Work with the index from the other side of the connection:
if (!isnull(other_connection.i)) {
/* do something */
}
# Data Types
Data types are assigned automatically. All types are value types, there are no reference types in RoomleScript, which is in conformity with the basic concept of the component update process.
Example:
arr1 = [10, 20];
arr2 = arr1; /* no reference types => makes copy or arr1 */
pushBack(arr1, 30); /* arr1 is [10, 20, 30] */
pushBack(arr2, 40); /* arr2 is [10, 20, 40] */
# Boolean
Values are true and false. These are internally handled as integers with values 1 and 0.
Example:
- Boolean variables
isRoot = true;
if (isRoot) {
/* ... */
}
hasRightArmrest = in(elementType, 'sofa', 'armchair', 'inlinearmrest_right', 'longchair_right');
- using advantage of internal data type
totalWidth =
hasLeftArmrest * armrestWidth + width + hasRightArmrest * armrestWidth;
/* which is the same as */
totalWidth =
(hasLeftArmrest ? armrestWidth : 0) +
width +
(hasRightArmrest ? armrestWidth : 0);
# Integer
Integers are internally handled as the long data type. Integers stay integers as long as there is no need to convert them to float, for example with floating point functions, like fabs. This is important to realize when working with large numbers.
New in 2023: In order to keep values stored in Integer type parameters as integers or for defining an integer as an internal value, you can use i suffix for numeric literals to force them as integers. Example:
{
"id": "minexamples:integers",
"label": "
label = 'Float literal: ' | 100 | ' Integer literal: ' | 100i;
// prints: Float literal: 100.00 Integer literal: 100
",
"parameters": [
{
"key": "intConst",
"type": "Integer",
"defaultValue": 10,
"label": "
'intConst: ' | intConst
// prints: intConst: 10
",
"visible": true
},
{
"key": "fltConst",
"type": "Decimal",
"defaultValue": 10,
"label": "
'fltConst: ' | fltConst
// prints: fltConst: 10.00
",
"visible": true
}
]
}
# float (data type)
Floats are internally handled as single precision floating point numbers (32 bits) and are precise up to about 7 digits.
Any number is considered to be a float by default, unless it has an i suffix (i.e. 100i) or comes from a parameter, which type is Integer.
You can use equality operation on floats safely up to three decimal spaces.
Example:
1.122 * 2 == 2.244; /* evaluates as true */
1.122 * 2 == 2.245; /* evaluates as false */
/* warning: following are not guaranteed to be precise */
1.12233 * 2 == 2.24466; /* evaluates as true */
1.1224 * 2 == 2.2447; /* evaluates as true (!) */
1.1223 * 2 == 2.2447; /* evaluates as false (!) */
# String
Strings can be delimited by single ' or double " quotes. However, as the scripts in the JSON files are also delimited with double quotes, those must be escaped \".
It is highly recommended to use single quote delimited strings as the primary choice for obvious reasons.
# Arrays
RoomleScript currently newly supports array of all data types. The type of array is determined by the strongest datatype stored inside at the time of initialization. Strength of data types is ascending as follows: boolean, integer, float, string.
You can insert a weaker datatype to an array, but you can not insert a value that has a stronger datatype than the array.
Array initialization:
arr1 = []; /* empty array */
arr2 = [10, 20]; /* array of consts */
offset1 = 100;
offset2 = 150;
offset3 = 200;
arr3 = [
offset1,
offset2,
offset3,
]; /* arrays initialized by variables by values (not by reference) */
offset1 = 200; /* arr3 stays [100, 150, 200] */
Use get and set functions for accessing array elements. Use stringToArray to parse a string containing an array (as of 2023, only array of floats is supported in the stringToArray function).
# Vector2f
A struct for holding a 2D float value. Components of the vectors are accessible via the xFromVector and yFromVector. String containing a Vector2f can be parsed via the stringToVector2f.
Usage:
v = Vector2f{100, 200};
# Vector3f
Usage is the same as Vector2f, just with an extra component accessible via the zFromVector function. A String containing a Vector3f can be parsed via the stringToVector3f.
# Keywords
# if - else if - else
Usage:
if (condition1) {
/* ... */
} else if (condition2) {
/* ... */
} else {
/* ... */
}
# for
Standard for loop. If script in which the loop is used has a write access, it is recommended to use the local _ scope prefix.
Usage:
for (_.i = 0; _.i < iterations; _.i++) {
/* ... */
}
# break
Useful in the for loop to immediately exit the current loop.
Usage:
for (_.i = 0; _.i < 100; _.i = _.i + 1) {
if (_.i == 20) {
break;
}
}
# continue
Useful in the for loop to immediately skip to the next iteration.
Usage:
for (_.i = 0; _.i < length(arr); _.i++) {
_.v = get(arr, _.i);
if (_.v == 0) {
continue;
}
pushBack(arr2, _.v);
countValid++;
}
# return
Immediately terminates execution of the current script. If script has an internal value to store the result (like label or condition), you can use return to assign to it.
Usage:
- In a
conditionscript
condition = true;
if (connection.isPreview && !frontSideIsVisible) {
return false; /* assigns to `condition` and terminates script */
}
- In the
numberInPartListscript
if (hasWalls) {
return wallsCount; /* assigns to `number` and terminates script */
} else {
number = 0; /* assigns to `number` */
return; /* terminates script */
}
- In any script
if (allDone) {
return; /* terminate immediately */
}
/* or continue doing something */
# Operators
| Precedence | Operator | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | - a, + a | Unary plus and minus |
| 2 | !a | Logical NOT |
| 3 | a++ | Suffix/postfix increment |
| 4 | a * b, a / b, a % b | Multiplication, division and modulo |
| 5 | a + b, a - b, a \| b | Addition, subtraction and concatenation |
| 6 | a >= b, a <= b, a > b, a < b | Relational operators < and ≤ and > and ≥ respectively |
| 7 | a == b, a != b | Equality operators = and ≠ respectively |
| 8 | a && b | Logical AND |
| 9 | a \|\| b | Logical OR |
| 10 | a ? b : c | Ternary conditional |
Refer to the fmod for the floating point modulo function.
# Comments
Commented code is ignored. Meta directives and commands exist. To learn more, refer to Tools and Importer Meta Keywords
# Single line comments
Single line comments can start with // or #.
// this is a single line comment
# this is a single line comment as well
WARNING
Using single line comments tends to break components while side loading from local drive for testing. For this reason, // style comments are converted to /* */ style comments by the Roomle Component Tool / roomle-content-tool-api format function.
# Multi-line comments
/*
this is a
multiline comment
*/
# Scope and Context of Variables
The default scope of any internal variable or parameter is the whole current component. Some scripts have read/write access to the component data, some scripts only have read access. To find out which scripts can access which context, you can refer to the [Script Access Rights] chapter.
RoomleScript also provides contexts on several occasions. This is an overview of them:
| prefix | availability | purpose |
|---|---|---|
| nothing | current component if script has WRITE access, otherwise current script | |
_. | local - current script | Use this for local helper variables. Variable will be set to null after current script finishes. |
parameter. | onValueChange and onUpdate script of the parameter | provides userTriggeredChange : boolean getter |
other. | all scripts in connections (onUpdate, condition, assigmentScripts) | access to all parameters and internal vars of the component on the other side of the connection |
self. | all scripts in connections (onUpdate, condition, assigmentScripts) | actually is redundant, but helps to understand the code unambigously and should be used whenever other. is used |
connection. | all scripts in connections (onUpdate, condition, assigmentScripts) | provides index, position, isPreview There are two connections in one docking/sibling point dock pair, one on each side. You can store and read variables relevant to the connection at the self side |
other_connection. | all scripts in connections (onUpdate, condition, assigmentScripts) | Same as before, but targets the other side of the connection. |
# Internal values
Some scripts have internal values defined. See the table and their purpose:
| identifier | context | purpose |
|---|---|---|
| articleNr | articleNr script | sets the current component's article number |
number | subComponent.numberInPartList | sets the subcomponent's count of entries in the part list |
connection.isPreview | docking condition | read-only, returns true if in docking preview state |
connection.index | docking range | returns the index of the docking point in the range array |
connection.position | docking range, line | returns Vector3f position of the child relative to the parent's coordinate system |
condition | all conditions | sets the result of the condition |
label | all label scripts | Has value from the labels map in the current language. Overwrite with value based on the script |
language | all label scripts | Getter for the language ISO code of the current locale the configurator runs with. |
parameter.userTriggeredChange | parameter.onValueChange script | getter to determine if the user has just interacted with this parameter |
# Functions
As of beginning of 2024, RoomleScript has a possibility to declare custom functions. As of Q2 2024, component scoped functions are provided.
Every function in RoomleScript is executed in the context of the script from which the function has been called. Therefore, functions can get or set values with the same rights as the script from which the function has been called. If a variable or a parameter exists and gets assigned in the scope of the function, its value is overwritten. Based on the access rights of the script, the variable is either changed for the current script only or for the whole component (the self context). If the script doesn't have write access rights, the parameter or variable get shadowed with a local variable. If no parameter or no variable in the scope of the function exists and there is an assignment to a new variable, it will be declared as an internal varaible of the function.
Function's parameters are always declared for the function and should not shadow variables or parameters in the scope where the function resides (be it a component.function or local function). A warning will be thrown if this is the case.
Functions can be nested (functions called within other functions), but can not be recursive (function calls the itself directly or indirectly).
Recommendation: Always use the context when working with function. Always use _. or self. prefixes inside the functions. This will avoid errors caused by suddenly adding a conflicting variable in the future. Let only the function's parameters stay without the context.
# Component Functions
Functions can be declared in the component.functions array. Such functions are then declared for the whole component and accessible based on their type attribute. Based on core-provided functions or contexts in the function, either of the four types have to be specified. Complex functionality can be defined for the component, which can save a lot of repeating code and related coding problems and also enables an API-like design approach to component creation.
{
"id": "example:function",
"functions": [
{
"key": "SumOfTwoNumbers",
"type": "default",
"arguments": [
{
"key": "a"
},
{
"key": "h"
}
],
"script": "return a + b;"
}
],
"onUpdate": "
self.x = SumOfTwoNumbers(100, 200);
"
}
The attributes of a function object are:
keyThe identifier of the function that will be used for calling it.typedefaultif not set, this is the default value. Useful for functions that do general computations.geometryRequired for functions containing geometry objects calls, like AddCube functionchangeableSupportssetBoxForMeasurement,setVisible,setEnabledonUpdateSupports requestDockItem andchangeablefunctionscollisionConditionFor accessing the collisionCondition functions are getters that are available in theconnection.collisionConditionscript:getBoxOrigin,getBoxSize,getBoxForMeasurementOrigin,getBoxForMeasurementSize
argumentsArray of function parameters:keyThe key to access the argument inside the functiondefaultValueIf set, the argument is non-mandatory in the function call (the defaultValue is used instead) and also allows using a keyword argument.
scriptThe body of the function. The keywordreturnterminates the function and if a value follows, it is returned.
Following function Sum can be called with any amount of arguments up until 5, i.e. Sum(1, 2) or Sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).
{
"key": "Sum",
"type": "default",
"arguments": [
{
"key": "num0",
"defaultValue": 0
},
{
"key": "num1",
"defaultValue": 0
},
{
"key": "num2",
"defaultValue": 0
},
{
"key": "num3",
"defaultValue": 0
},
{
"key": "num4",
"defaultValue": 0
}
],
"script": "
return num0 + num1 + num2 + num3 + num4;
"
}
Following function call uses the keyword arguments:
{
"id": "tests:componentfunctions",
"functions": [
{
"key": "AddBoardWithHole",
"type": "geometry",
"arguments": [
{
"key": "cubeSize"
},
{
"key": "cubeColor",
"defaultValue": "isdt:wood_oak"
},
{
"key": "holeDiameter",
"defaultValue": 100
},
{
"key": "holeColor",
"defaultValue": "testing101:mr_chipboard"
}
],
"script": "
_.w = cubeSize;
_.h = 30;
_.d = cubeSize / 2;
AddCube(Vector3f{_.w, _.d, _.h});
SetObjSurface(cubeColor);
if (holeDiameter < _.d) {
_.r = holeDiameter / 2;
AddCylinder(_.r, _.r, 2 * _.h, 16);
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{_.w / 2, _.d / 2, 0});
SetObjSurface(holeColor);
MinusOperator();
}
"
},
{
"key": "Array_Sum",
"type": "default",
"arguments": [
{
"key": "array"
}
],
"script": "
_.sum = 0;
for (_.i = 0; _.i < length(array); _.i = _.i + 1) {
_.sum = _.sum + get(array, _.i);
}
return _.sum;
"
}
],
"onUpdate": "
self.sum = Array_Sum([100, 400, 500]);
",
"geometry": "
AddBoardWithHole(self.sum, 'isdt:black', 400, 'isdt:white');
AddBoardWithHole(self.sum);
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{self.sum, 0, 0});
AddBoardWithHole(self.sum, holeColor = 'isdt:yellow'); // keep cubeColor and holeDiameter default, set holeColor
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{2 * self.sum, 0, 0});
"
}
# SubComponent Functions
If component.functions are defined, they can be accessible in the subComponent. Keep in mind, that the functions are evaluated not in the subComponent, but in the current component, as if they were just copied to the current component's functions array. In this case, the functions should be prefixed with the subComponent's internalId. See following example where the functions are referred and used by another component.
{
"id": "tests:subcomponentfunctions",
"subComponents": [
{
"internalId": "Functions",
"componentId": "tests:subcomponentfunctions",
"active": false
}
],
"onUpdate": "
self.sum = Functions.Array_Sum([100, 400, 500]);
",
"geometry": "
Functions.AddBoardWithHole(self.sum, 'isdt:black', 400, 'isdt:white');
Functions.AddBoardWithHole(self.sum);
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{self.sum, 0, 0});
Functions.AddBoardWithHole(self.sum, holeColor = 'isdt:yellow');
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{2 * self.sum, 0, 0});
"
}
Notice, that the subComponent is not active. If a subComponent only carries functions or data and is not expected to be a part list entry or a geometry subComponent, there is no point for it to remain active.
Such feature allows you to create a component with a library of functions that can be linked to other components.
However, if the functions in the subComponent are nested, they need to be called in the correct context, which is a complication and will be solved with a feature in the future.
# Custom Local Functions
Local functions can be defined using the function keyword, very similarly as it is done in JavaScript. Local functions are valid only in the script where they are declared and all calls of it must be done behind its declaration.
Examples:
x = getFive(); // error, function is used before its declaration
function getFive() {
return 5;
}
y = getFive(); //
{
"onUpdate": "
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
",
"geometry": "
AddCube({add(2 + 3) * 100, 100, 100}); // error - function add is not declared in the geometry script
"
}
{
"id": "tests:functions",
"parameters": [
{
"key": "num",
"type": "Integer",
"visible": true,
"validValues": [
1,
2,
5
]
}
],
"onUpdate": "
function setNum(n) {
self.num = n;
}
setNum(2); // will set the parameter num to 2
",
"geometry": "
AddCube({self.num * 1000, 1000, 1000}); // result: 2000, 1000, 1000
function setNum(n) { // function declarations will not conflict since they are local; this is, however, not a good practice
self.num = n;
}
setNum(5); // will not set the parameter num to 5, instead will create a internal variable in the geometry script under the identifier num which shadows the parameter from that place on
AddCube({self.num * 1000, 1000, 1000}); // result: 5000, 1000, 1000
MoveMatrixBy({0, 1000, 0});
"
}
# Constants
| Constant | Value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
M_E | 2.71828 | Euler constant |
M_LOG2E | 1.44270 | base 2 logarithm of M_E |
M_LOG10E | 0.42429 | log10(M_E) |
M_LN2 | 0.69315 | log(2) |
M_LN10 | 2.30259 | log(10) |
M_PI | 3.14159 | π |
M_PI_2 | 1.57080 | M_PI / 2 |
M_PI_4 | 0.78540 | M_PI / 4 |
M_1_PI | 0.31831 | 1 / M_PI |
M_2_PI | 0.63622 | 2 / M_PI |
M_2_SQRTPI | 1.12838 | 2 / sqrt(M_PI) |
M_SQRT2 | 1.41421 | sqrt(2) |
M_SQRT1_2 | 0.70711 | sqrt(2) / 2 or sin(M_PI / 6) or sine of 30 degrees / cosine of 60 degrees |
Convert degrees to radians: a * M_PI / 180
Convert radians to degrees: a * 180 / M_PI
# Available Functions
List of available functions in all RoomleScripts of the component definition.
# acos
(a: float) : float
Arcus cosine (arccosine)
Parameters:
a: float value between -1 and 1
Returns: arccosine of a in radians.
Usage:
v = 0.5;
angleRad = acos(v); /* returns 1.04719755 */
angle = (angleRad / M_PI) * 180; /* 60 */
# activeGroupInView
() : String
Queries the configurator UI to get the currently selected parameter group. This is useful for manipulating geometry based on what the user is configuring.
Returns: key property of the current parameter group
Usage:
- onUpdate:
displayOpenDoor = activeGroupInView() === 'grpInternalEquipment';
- geometry:
AddCube(Vectorf3{doowWidth, doorThickness, doorHeight});
if (displayOpenDoor) {
/* rotate the door to visualize it is open */
RotateMatrixBy(Vector3f{0, 0, 1}, Vector3f{0, 0, 0}, 105);
}
# asin
(a: float) : float
Arcus sine (arcsine)
Parameters:
a: value between -1 and 1
Returns: arcsine of a in radians.
Usage:
v = 0.5;
angleRad = asin(v); /* returns 523598776 */
angle = (angleRad / M_PI) * 180; /* 30 */
# atan
(a: float) : float
Arcus tangent.
Parameters:
a: value between -1 and 1
Returns: arctangent of a in radians.
# atan2
(y: float, x: float) : float
Arcus tangent defined by ratio of opposite and adjacent side of the triangle.
Parameters:
y: length of opposite sidex: length of adjacent side
Returns: arctangent of the angle in radians.
# ceil
(number: float, digits: float) : float
Nearest higher value
Parameters:
number: the number to be ceileddigits: count of decimal digits
Returns: Nearest higher value rounded to given amount of decimal spaces.
Usage:
x = 123.4567;
ceil(x, 0); /* returns 124 */
ceil(x, 2); /* returns 123.46 */
# cos
(valueRad: float) : float
Cosine
Parameters:
valueRad: value in radians
Returns: cosine value of a.
# cosh
(valueRad: float) : float
Hyperbolic cosine
Parameters:
valueRad: value in radians
Returns: hyperbolic cosine value of a.
# exp
(x: float) : float
Exponential function
Parameters:
x: the exponent
Returns: Value of e powered to x
# fabs
(x: float) : float
Absolute value
Parameters:
x: value
Returns: x if x is positive or -x if x is negative.
Usage:
fabs(5); /* returns 5 */
fabs(-5); /* returns 5 */
# float
(value: any) : float
Convert to float
Parameters:
valuethe value to try to convert to float
Returns: If value starts with number, returns the first parsed number, otherwise 0.
Usage:
float('5'); /* returns 5.0 */
float('5 hello 3432'); /* returns 5.0 */
float('5.3'); /* returns 5.3 */
float('5,3'); /* returns 5.0 */
float(' 5'); /* returns 5.0 */
float('_5'); /* returns 0.0 */
float([5]); /* returns 0.0 */
float([1]); /* returns 0.0 */
float(Vector3f{5,5,5}) /* returns 0.0 */
# floor
(number: float, digits: float) : float
Nearest lower value
Parameters:
number: the number to be flooreddigits: count of decimal digits
Returns: Nearest lower value rounded to given amount of decimal spaces.
Usage:
x = 123.4567;
floor(x, 0); /* returns 123 */
floor(x, 2); /* returns 123.45 */
# fmod
(dividend: float, divisor: float) : float
Floating point modulo
Parameters:
dividend: floatdivisor: float
Returns: Modulo as float.
Warning Works well only with integers that can be represented by single precision floating point numbers (32 bits, up to around 7 digits).
Usage:
fmod(13, 4); /* returns 1 */
fmod(12, 4); /* returns 0 */
fmod(123456789, 1234567); /* will not work well */
# get
(array: [float], index: Integer) : float
Reads an array element at a given index.
To write an array element, refer to set.
Parameters:
array: the array you want to accessindex: index of the element in the array, index of the first element is zero0- ⚠️ float indices will floor to the next lower integer
Returns: The number from the array at the given index or 0 if fails.
Throws:
[1404]Index out of bounds. Returns 0 in this case, execution continues
Usage:
arr = [10, 20, 30, 40];
get(arr, 2); /* returns 30 */
get(arr, 2.9); /* returns 20 */
get(arr, 2.999999); /* returns 20 */
get(
arr,
2.9999999
); /* returns 30 (floating point precision flips to index 3) */
get(arr, 5); /* returns 0, throws 1404 */
get(arr, -1); /* returns 0, throws 1404 */
# getComponentProperty
(propertyKey: 'runtimeId' | 'externalId' | 'catalogId', runtimeId*: integer) : integer | string
Returns the unique runtime id, or component Id of the current component. If this function is used in a collisionCondition script, such a property of another colliding component can be retrieved.
Note: parts of an ID are catalogId:externalId
Parameters:
propertyKeyeitherruntimeId,externalIdorcatalogIdstring valuesruntimeIda runtime ID of a different component, only availabe in thecollisionCondition
Returns:
- unique runtime ID as an integer
- external or catalog ID as a string
Usage:
id = getComponentProperty('runtimeId'); // equivalent to getUniqueRuntimeId()
componentId =
getComponentProperty('catalogId') | ':' | getComponentProperty('externalId');
"collisionCondition": "
for (i = 0; i < length(collidingComponentIDs); i++) {
collidingComponentId = get(collidingComponentIDs, i);
// avoid collision with the catalog:shelf component
if (getComponentProperty('externalId', collidingComponentId) == 'shelf') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
"
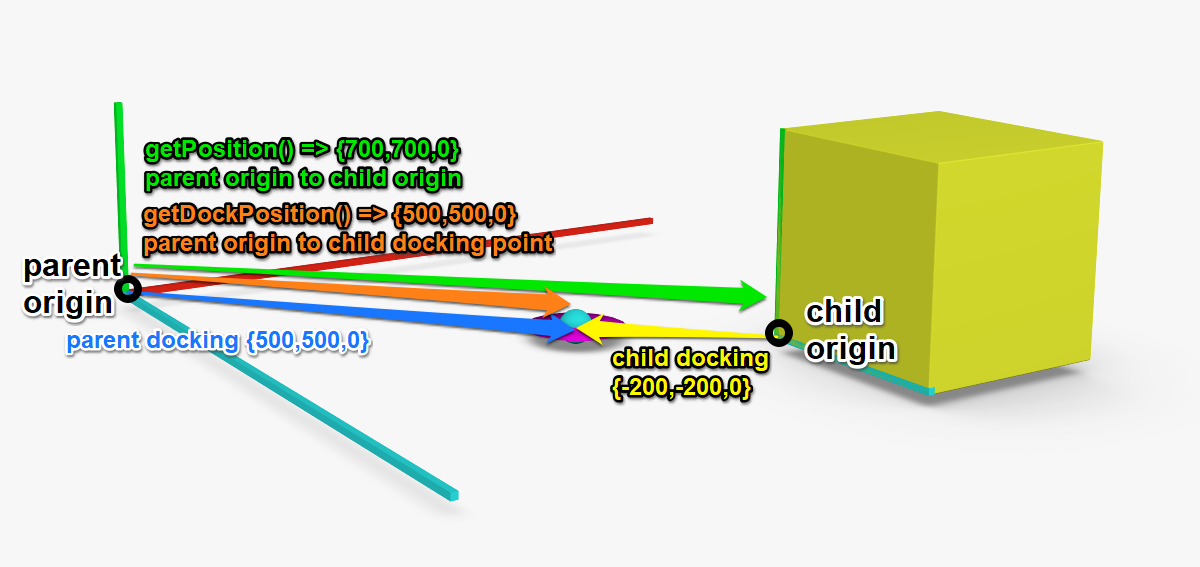
# getDockPosition
() : Vector3f
Get position of child docking point in the coordinate system of the parent.
Returns: Vector from parent origin to child docking point or zero Vector3f if component is the root component.
See getPosition for more details.
# getDockPositionRelativeToParentDock
() : Vector3f
Get position of the child docking point in the coordinate system of the parent relative to the parent docking point.
Returns:
- point - point: ideally zero Vector3f or the offset if configuration doesn't reload properly
- range - point: ideally zero Vector3f or the offset if configuration doesn't reload properly
- line - point: Vector from the beginning of the dockLine to the child docking point
- root: zero Vector3f
# getMaterialProperty
(materialId: String, propertyName: String, fallback: String) : String
Retrieves additional material data defined in material properties. See Using GetMaterialPropery Function for detailed description.
Parameters:
materialId: Id of the target materialpropertyName: name of the property on the given materialfallback: Value to return if material or property are missing
Returns: the value stored in the material property or fallback if no material is found or if the material doesn't have the property.
Usage:
- exmaple material entry:
{
"externalIdentifier": "fabric_blue",
"id": "isdt:fabric_blue",
"properties": {
"pricegroup": "30"
},
...
}
getMaterialProperty('isdt:fabric_blue', 'pricegroup', 'NULL'); /* returns '30' */
getMaterialProperty('isdt:fabric_blue', 'type', 'NULL'); /* returns 'NULL' */
getMaterialProperty('doesnt:exist', 'something', 'NULL'); /* returns 'NULL' */
# getPosition
() : Vector3f
Get position of the child component in the coordinate system of the parent.
Returns: Vector3f leading from parent component origin to child component origin or zero Vector if component is the root component.
Usage:
position = getPosition();
parentOrigin = Vector3f{
- xFromVector(position),
- yFromVector(position),
- zFromVector(position)
};
# getUniqueRuntimeId
() : Integer
Returns unique runtime ID that has been assigned to this component instance in the configurator. Every root component, child component and subComponent will have an unique number. This number is not reused after for example deleting components. It is not persistent between configuration instances. Can be used to determine the timing order in which the components have been added to the configuration.
It is useful as a decision factor between two components connected via sibling points in cases that no other way to choose one component from more.
This number is not persistent between configurator instances (i.e. after configuration reload or between undo/redo actions) and in most cases, storing it as a parameter makes no sense and can lead to errors.
Example: See the Quadpost Shelf System template
Returns: Integer representing the unique runtime ID of the component in the configuration.
Usage:
/* in onUpdate */
if (isnull(uid)) {
/* enter only in the first onUpdate call */
uid = getUniqueRuntimeId(); /* could be for example 7 */
}
/* in a siblingPoint.assignmentScripts.onUpdate script to determine owner of the shared wall */
if (self.height > other.height) {
self.hasSharedWall = true;
} else if (self.height < other.height) {
self.hasSharedWall = false;
} else {
self.hasSharedWall = self.uid > other.uid;
}
# ifnull
(variable: any, fallback: any) : any
Checks if a variable is undefined or null and returns the variable or fallback. Useful for making sure a variable is defined.
Parameters:
variable: the variable to check for nullfallback: a value to return if varialbe is null or undefined
Returns:
- either the
variableor thefallbackifvariableis null
Usage:
/* checks if variable 'initialized' is null and if yes, returns true in order to enter the block */
if (ifnull(initialized, true)) {
/* make sure to initialize in order to enter only once */
initialized = true;
}
# in
(valueToCheck: any, value1: any, value2: any, ...) : boolean
Useful for checking if a list of values containes a specific value.
Parameters:
valueToCheck: the value that is being searched for in the listvalueN: any number of arguments that will form the list
Returns
trueif valueToCheck is equal to at least one of the other values, otherwisefalse
Usage:
fruit = 'banana';
isFruit = in(fruit, 'apple', 'banana', 'cherry'); /* true */
pearIsValid = in('pear', 'apple', 'banana', 'cherry'); /* false */
Most used to compare a variable to a list of constants, however you can also check a constant to a list of variables.
/* check if at least one of variables is true */
isGroceryItem = in(true, isFruit, isVegetable, isDairy);
/* which is actually equivalent to */
isGroceryItem = (isFruit + isVegetable + isDairy) > 0;
# inArray
(searchedValue: float, array: [float]) : Boolean
Checks if array contains a value.
Arguments
searchedValue: the value that is being looked forarray: the array to check
Returns: True if array contains the value.
Usage:
inArray(1, [1, 2, 3, 1]); /* returns 1 */
inArray(10, [1, 2, 3, 1]); /* returns 0 */
# indexOf
(searchedValue: float, array: [float]) : Integer
Find index of a value in an array.
Parameters:
searchedValue: the value that is being looked forarray: the array to search
Returns: Index of the first occurence of the value in the array or -1 if no occurence.
Usage:
indexOf(1, [1, 2, 3, 1]); /* returns 0 */
indexOf(10, [1, 2, 3, 1]); /* returns -1 */
# insert
(array: [float], index: Integer, value: float | [float]) : void
Insert into array in front of the element at given index
Parameters:
array: array into which the values are insertedindex: index of the element before which the values will insertvalue: value to be inserted, can be a number or an array of numbers
Throws:
[1404]index out of bounds
Usage:
arr = [10, 20];
insert(arr, 1, 15); /* arr is [10, 15, 20] */
insert(arr, 0, [0, 5]); /* arr is [0, 5, 10, 15, 20] */
insert(arr, 5, 25); /* arr stays [0, 5, 10, 15, 20], throws [1404] */
insert(arr, -1, 5); /* arr stays [0, 5, 10, 15, 20], throws [1404] */
# intersection
(a: [float], b: [float]) : [float]
Intersection of arrays
Parameters:
a,b: two arrays of numbers
Returns: Array with elements that are present in both arrays.
Usage:
intersection([3, 2, 1], [2, 3, 4, 5]); /* returns [2, 3] */
intersection([3, 2, 1], [5, 4, 3, 2]); /* returns [3, 2] */
intersection([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]); /* returns [] */
intersection([1], [1, 1, 1]); /* returns [1, 1, 1] */
intersection([1, 1, 1], [1]); /* returns [1, 1, 1] */
# isEnabled
(parameterKey: String) : Boolean
Returns if a parameter is enabled.
Parameters:
parameterKey: key of the parameter
Returns: True if the parameter exists and its enabled flag is true, false otherwise.
Usage:
if (isVisible(depth)) {
actualDepth = depth;
} else {
/* do not take the depth parameter value but a fallback */
actualDepth = 700;
}
# isnull
(value: any) : Boolean
Checks for null values.
Parameters:
value: identifier to be checked
Returns: True if identifier is undeclared, null or after setnull call.
Usage:
- initialize on component load, at the beginning of onUpdate
if (isnull(initialized)) {
initialized = true;
/* initialize values here */
}
- in a connection script of a docking range:
/* compute indeces of the docking point */
if (isnull(connection.i)) { connection.i = xFromVector(connection.position) / > offset; }
if (isnull(connection.j)) { connection.j = yFromVector(connection.position) / > offset; }
# isVisible
(parameterKey: String) : Boolean
Returns if a parameter is visible.
Parameters:
parameterKey: the parameter key to get the visible flag value from
Returns: True if the parameter exists and its enabled flag is true, false otherwise.
Usage:
if (isVisible(depth)) {
actualDepth = depth;
} else {
/* do not take the depth parameter value but a fallback */
actualDepth = 700;
}
# length
(array: [float])
Length of array (for the length of a String, refer to size).
Parameters: * array: array of floats
Returns: count of the array elements.
Usage:
a = [];
b = [0, 1, 2];
c = [0];
length(a); /* returns 0 */
length(b); /* returns 3 */
length(c); /* returns 1 */
# like
(input: String, pattern: String) : Boolean
Returns true if input matches the pattern. The pattern is a String with placeholders for one any single character or any subString.
This is the OPTION_LIKE operator from the IDM 3.1 standard, which itself is based to be similar on the SQL's LIKE operator.
Parameters:
input: the String to check against the patternpattern: a case sensitive String pattern, where_is a wildcard for any single character and%is a wildcard representing any subString at least 1 character longa_- length 2, starts withaa%- any String starting witha_a- length 2, ends witha%a- any String that ends with a%a%- any String that containsa
Returns: true if String matches to the pattern, otherwise false
Usage:
like('Hello beautiful world', 'Hello'); /* false; no wildcard, pattern means equls to 'Hello' */
like('Hello beautiful world', 'Hello%'); /* true; pattern means starts with 'Hello' */
like('Hello beautiful world', '%beatiful%'); /* true; pattern means contains 'beatiful' */
like('Hello beautiful world', '%Hello%'); /* false; pattern means contains 'Hello' which is preceded and followed by other characters */
like('Hello beautiful world', 'Hello%world'); /* true; pattern means starts with 'Hello' and ends with 'world' */
like('Hello beautiful world', 'h%'); /* false; pattern means starts with 'h' */
# log
(value: float) : float
Natural logarithm
Parameters:
value
Returns: Logarithm of the value with base of e (~2.718)
Usage:
log(100); /* returns ~4.605 */
log(M_E); /* returns 1 */
log(1); /* returns 0 */
log(0); /* returns -inf */
# log10
(value: float) : float
Common logarithm
Parameters:
value
Returns: Logarithm of the value with base of 10
Usage:
log10(100); /* returns 2 */
log10(M_E); /* returns ~0.434 */
log10(1); /* returns 0 */
log10(0); /* returns -inf */
# popBack
(array: [float]) : float
Returns and removes last number from array.
Parameters:
array
Returns: Last number of array, original array has this value removed or 0 if [1405] is thrown.
Throws:
[1405]: popBack empty array
Usage:
arr = [10, 20];
x1 = popBack(arr); /* returns 20, arr is [10] */
x2 = popBack(arr); /* returns 10, arr is [] */
x3 = popBack(arr); /* returns 0, arr is [], throws [1405] */
# pow
(value: float, exponent: float) : float
Power function
Parameters:
value: the value to compute powerexponent
Returns: value powered to exponent.
# pushBack
(array: [float], value: float) : void
Pushes a value at the end of an array.
Parameters:
array: the array to which to pushvalue: the value to push
Usage:
arr = [];
for (_.i = 0; _.i < 5; _.i = _.i + 1) {
pushBack(arr, 0);
}
/* arr is [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] */
# removeAt
(array: [float], index: Integer) : float
Remove element at index from an array and return the next.
Parameters:
array: the array from which the element should be removedindex: index at which to remove the element, first index is 0
Returns: Next element after the one that has been removed or 0 if the element is the last one or if [1404] has been thrown.
Throws:
[1404]: Index out of bounds
Usage:
arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
x1 = removeAt(arr, 2); /* returns 40, arr is [10, 20, 40, 50] */
x2 = removeAt(arr, 3); /* returns 0, arr is [10, 20, 40] */
x3 = removeAt(arr, 3); /* returns 0 and throws 1404, arr stays as it is */
x3 = removeAt(arr, -1); /* returns 0 and throws 1404, arr stays as it is */
# requestDockItem
(configuration: string, parentDockPointPosition: Vector3f, childDockPointPosition: Vector3f)
Sends a docking request to the configurator. After the current update call will have been finished, a docking of the defined configuration will happen. Connection and child component will be available in the next update call. Because the docking does not happen in the configurator kernel, compatible version of the SDK has to be used in custom integration for this function to be available. You need to define which docking points to use on both side by their positions.
This function is only valid in the main onUpdate script and must be inside an if-block.
Parameters:
configurationEither an itemId or a stringified configuration JSON that should dock.parentDockPointPositionVector3f containing coordinates of a valid docking point on the parent side.childDockPointPositionVector3f containing coordinates of the child docking point.
Hint: To find out the correct arguments, you can do the docking manually and then check the configuration (which can be achieved by calling RoomleConfigurator.getCurrentConfiguration() or by using the interface buttons of the Rubens CLI). The parent docking point argument is the dockPosition of the child component, the child docking point is the dockChild value of the child component.
Usage:
requestDockItem('catalog:itemId', Vector3f{width / 2, 0, 0}, Vector3f{ -300 /* -width/2 of the child */, 0, 0 });
requestDockItem('{\"componentId\":\"catalog:componentId\"}', Vector3f{width / 2, 0, 0}, Vector3f{ -300 /* -width/2 of the child */, 0, 0 });
# round
(number: float, digits: float) : float
Nearest rounded value
Parameters:
number: the number to be roundeddigits: count of decimal digits
Returns: Nearest value rounded to given amount of decimal spaces.
Usage:
x = 1.234567;
round(x, 0); /* returns 1 */
round(x, 1); /* returns 1.2 */
round(x, 2); /* returns 1.23 */
round(x, 3); /* returns 1.235 */
round(x, 4); /* returns 1.2346 */
# set
(array: [float], index: Integer, value: float) : void
Sets value of an array element at a given index.
Parameters:
array: the array you want to setindex: index of the element in the array, index of the first element is zero0- ⚠️ float indices will floor to the next lower integer
value: the new value that will replace the old value
Throws:
[1404]Index out of bounds.
Usage:
arr = [1, 2, 3];
set(arr, 0, 5); /* [5, 2, 3] */
set(arr, 1, get(arr, 2)); /* [5, 3, 3] */
set(arr, 2, get(arr, 2) + 1); /* [5, 3, 4] */
# setBoxForMeasurement
(size: Vector3f, position: Vector3f) : void
Overrides the bounding box of the geometry in order to change the measurements.
⚠️ This is only valid if called in onUpdate
Parameters:
size: defines the size of the bounding boxposition: position of the left rear bottom corner of the box
Hint: This behaves like a combination of AddPlainCube and MoveMatrixBy. Refer to the Dimensioning chapter for more information and examples.
Usage:
setBoxForMeasurement(Vector3f{1600, 800, 670}, Vector3f{-800, 0, 0});
# setEnabled
(parameterKey: String, enable: Boolean) : void
Sets and overrides the enabled flag of the parameter with the given key. This applies for the update loop in which this call is done.
Parameters:
parameterKey: key of the parametervalue: final status of theenabledflag
Usage:
"parameters": [
{
"key": "width",
"type": "Decimal",
"defaultValue": 100,
"unitType": "length",
"enabled": true,
"validValues": [100, 200, 300]
}
],
"onUpdate": "setEnabled('width', false) /* disables the width parameter */"
# setnull
(variable: any) : void
Undeclares a variable of given name.
Usage:
setnull(x);
if (isnull(x)) { /* true */
...
}
# setVisible
(parameterKey: String, enable: Boolean) : void
Sets and overrides the visible flag of the parameter with the given key. This applies for the update loop in which this call is done.
Parameters:
parameterKey: key of the parametervalue: final status of thevisibleflag
Usage:
"parameters": [
{
"key": "width",
"type": "Decimal",
"defaultValue": 100,
"unitType": "length",
"visible": true,
"validValues": [100, 200, 300]
}
],
"onUpdate": "setVisible('width', false) /* hides the width parameter */"
# sin
(valueRad: float) : float
Sine
Parameters:
valueRad: value in radians
Returns: sie value of a.
# sinh
(valueRad: float) : float
Hyperbolic sine
Parameters:
valueRad: value in radians
Returns: hyperbolic sine value of a.
# size
(input: String)
Length of String.
Parameters: * input: String
Returns: count of the String's characters.
Usage:
a = 'Hello';
b = '';
size(a); /* returns 5 */
size(b); /* returns 0 */
# sqrt
(number: float) : float
Square root
Parameters:
number: zero or positive number
Returns: Square root of the number or nan
Usage:
sqrt(2); /* returns M_SQRT2 or ~1.414 */
# string
(input: any, [decimalSpaces: Integer = 2]) : String
toString function - converts value to string.
Parameters:
inputvalue to stringifydecimalSpacesif input is an Integer or float, defines the amount of decimal spaces of the number to show; default is 2- note: not appliable to array, Vector2f, Vector3f, String
Returns: Value converted to string.
Usage:
string('some string') /* returns 'some string' */
string('some string', 4) /* returns 'some string' */
string(M_PI) /* returns '3.14' */
string(M_PI, 0) /* returns '3' */
string(M_PI, 2) /* returns '3.14' */
string(M_PI, 5) /* returns '3.14159' */
string([1, 2]) /* returns '[1.00,2.00]' */
string([1, 2], 0) /* returns '[1.00,2.00]' */
string(Vector2f{1, 2}) /* returns '{1.00,2.00}' */
string(Vector2f{1, 2}, 0) /* returns '{1.00,2.00}' */
string('1.00', 0) /* returns '1.00' */
string('1', 5) /* returns '1' */
# stringPart
(input: String, delimiter: String, index: Integer, *fallback: String)
Splits a string with a delimiter and returns the part under the given index.
Parameters:
input: the string intended to be parseddelimiter: a string that will be used to separate the input stringindex: index of the part that willfallback: optional value to return if fails, empty string''by default
Returns: part of the string or a fallback value (defined or '') if fails.
Usage:
id = 'abcd:efgh';
catalogueId = stringPart(id, ':', 0); /* returns 'abcd' */
externalId = stringPart(id, ':', 1); /* returns 'efgh' */
empty = stringPart(id, ':', 2); /* returns '' */
fallback = stringPart(id, ':', 2, 'NULL'); /* returns 'NULL' */
# stringToArray
(stringifiedArray: string) : [float]
Parses a string to array.
Parameters:
stringifiedArray: stirng in a[number, number, ...]pattern
Returns: The parsed array or null if failed.
Usage:
arr = stringToArray('[1,2,3]');
x = get(arr, 0); /* returns 1 */
# stringToVector2f
(stringifiedVector: string) : Vector2f
Parses a string as Vector2f.
Parameters:
stringifiedVector: String in aVector2f{number, number}or{number, number}pattern
Throws:
[1301]Error getting value
Returns: The parsed vector or null if failed.
Usage:
- Vector parameter
{
"key": "size",
"type": "String",
"valueObjects": [
{
"value": "{100,200}",
"labels": {
"en": "10 x 20"
}
},
{
"value": "Vector3f{1000,200}",
"labels": {
"en": "100 x 20"
}
}
]
}
_size = stringToVector2f(size);
AddCube(Vector3f{xFromVector(_size), yFromVector(_size), 500});
# stringToVector3f
(stringifiedVector: string) : Vector3f
Parses a string as Vector3f.
Parameters:
stringifiedVector: String in aVector3f{number, number, number}or{number, number, number}pattern
Throws:
[1301]Error getting value
Returns: The parsed vector or null if failed.
Usage:
- Vector parameter
{
"key": "size",
"type": "String",
"valueObjects": [
{
"value": "{100,200,300}",
"labels": {
"en": "10 x 20 x 30"
}
},
{
"value": "Vector3f{1000,200,300}",
"labels": {
"en": "100 x 20 x 30"
}
}
]
}
_size = stringToVector3f(size);
AddCube(Vector3f{xFromVector(_size), yFromVector(_size), zFromVector(_size)});
# substring
(input: String, startIndex: Integer, length: Integer) : String
Returns part of string based on position and length.
Parameters:
input: the string from which the substring is to be extracedstartIndex: index where the substring starts, first index is 0length: length of the substring
Returns: Part of string starting at the given index of the given length. Empty string is returned for every character that is outside of the string, rather than throwing an exception.
Usage:
substring('my string', 3, 6); /* returns 'string' */
substring('my string', 3, 0); /* returns '' */
substring('my string', -3, 6); /* returns '' */
substring('my string', -3, 6); /* returns '' */
substring('my string', 0, 100); /* returns 'my string' */
substring('my string', 10, 100); /* returns '' */
# tan
(valueRad: float) : float
Tangent
Parameters:
valueRad: value in radians
Returns: tangent value of a.
# tanh
(valueRad: float) : float
Hyperbolic tangent
Parameters:
valueRad: value in radians
Returns: hyperbolic tangent value of a.
# xFromVector
(v : Vector2f | Vector3f) : float
Get X component of a Vector
Parameters:
vthe vector
Returns: x component of the Vector or 0 if fails
Usage:
v2 = Vector2f{10, 20};
v3 = Vector3f{100, 200, 300};
x2 = xFromVector(v2); /* returns 10 */
x3 = xFromVector(v3); /* returns 100 */
# yFromVector
(v : Vector2f | Vector3f) : float
Get Y component of a Vector
Parameters:
vthe vector
Returns: X component of the Vector or 0 if fails
Usage:
v2 = Vector2f{10, 20};
v3 = Vector3f{100, 200, 300};
x2 = yFromVector(v2); /* returns 20 */
x3 = yFromVector(v3); /* returns 200 */
# zFromVector
(v : Vector3f) : float
Get Z component of a Vector
Parameters:
vthe vector
Returns: Z component of the Vector or 0 if fails
Usage:
v2 = Vector2f{10, 20};
v3 = Vector3f{100, 200, 300};
x2 = zFromVector(v2); /* returns 0 */
x3 = zFromVector(v3); /* returns 300 */
# getData functions
There are several functions that can retrieve data from a JSON contained in the component definition. This JSON is stored in the component.data field.
You can read the data and use them as a value using get* functions, or you can have the value of the JSON evaluated and treated as an expression using data context of your current script using the evaluate* functions. See evaluateData functions
getSubComponentData* and evaluateSubComponentData* do the same, but in context of a subComponent defined with an internal ID.
Non-existent data values are handled with the triplet of functions: plain *Data (like getData) only throw an error, *DataOrNull returns an actual null when data is not found and *WithDefault will return a fallback value, which is the last argument of the function.
See following with examples.
# getData
(arg1 : String | Integer, ... argN: String | Integer) : String | float | null
Retrieves data from the data storage JSON object in the component.data.
⚠️ This does not handle non-existing path and scripter needs to ensure that the requested path exists.
Attributes:
argN: key name as String or array index as Integer
Returns: The retrieved data or null.
Throws:
[1308]Data not found
Usage:
- define the
datain the component definition
{
"id": "test:data",
...
"data": {
"size": 300,
"colors": [
"isdt:red",
"isdt:green"
],
"elementTypes": {
"smallbox": {
"label": "Small Box"
},
"bigsphere": {
"label": "Big Sphere"
}
}
}
}
- retrieve them using the
getDatafunction
/* returns 300 */
width = getData('size');
/* returns 'isdt:green' */
color = getData('colors', 1);
/* returns the 'Small Box' or 'Big Sphere' based on the current value of elementType variable */
label = getData('elementTypes', elementType, 'label');
# getDataOrNull
(arg1 : String | Integer, ... argN: String | Integer) : String | float | null
Retrieves data from the data storage JSON object in the component.data or null if data wasn't found.
Attributes:
argN: key name as String or array index as Integer
Returns: The retrieved data or null.
Usage:
- define the
datain the component definition
{
"id": "test:data",
...
"data": {
"size": 300,
"colors": [
"isdt:red",
"isdt:green"
],
"elementTypes": {
"smallbox": {
"label": "Small Box",
"hasChildDock": true
},
"bigsphere": {
"label": "Big Sphere",
"hasParentDock": true
}
}
}
}
- retrieve them using the
getDataOrNullfunction in theconditionscript of aparentDocking
_.hasParentDock = getDataOrNull('elementTypes', elementType, hasParentDock);
if (isnull(_.hasParentDock) || _.hasParentDock == false) {
/* kill this docking if the element type has no docking possibility in the first step */
return false;
}
/* conitnue with the condition evaluation */
# getDataWithDefault
(arg1 : String | Integer, ... argN: String | Integer, fallback : any) : String | float | null
Retrieves data from the data storage JSON object in the component.data and returns a fallback value if entry hasn't been found.
Attributes:
argN: key name as String or array index as Integerfallback: value to return if target path doesn't exist
Returns: The retrieved data or fallback.
Usage:
- define the
datain the component definition
{
"id": "test:data",
"parameters": [
{
"key": "elementType",
"validValues": [
"armchair",
"inline"
]
}
],
...
"data": {
"translations": {
"armchair": {
"en": "Armchair",
"de": "Sessel",
"fr": "Fauteuil"
},
...
}
}
}
- retrieve them using the
getDataWithDefaultfunction in alabelscript:
return getDataWithDefault(
'translations',
elementType,
language,
getData('translations', elementType, 'en')
);
Note: language hold the ISO code of the current language. It can be es for example, in which case the translation entry doesn't exist. Because elementType has a list of validValues, the developer can make sure that the getData will always return a value.
# getSubComponentData
(subComponentInternalId : String, arg1 : String | Integer, ... argN: String | Integer) : String | float | null
Retrieves a component.data from another component, that is being linked as a subComponent of this component. Works exactly same as the getData counterpart, just in a different component.
Attributes:
subComponentInternalId: internalId of a subComponent definitionargN: key name as String or array index as Integer
Returns: The retrieved data or null.
Throws:
[1308]Data not found
Usage:
"subComponents": [
{
"internalId": "DATACOMPONENT",
"componentId": "mycatalog:component_with_data",
"active": false,
"numberInPartList": 0
}
]
getSubComponentData('DATACOMPONENT', 'elementTypes', 'chair', 'articleCode');
# getSubComponentDataOrNull
(subComponentInternalId : String, arg1 : String | Integer, ... argN: String | Integer) : String | float | null
OrNull counterpart of getSubComponentData. See getDataOrNull and getSubComponentData.
# getSubComponentDataWithDefault
(subComponentInternalId : String, arg1 : String | Integer, ... argN: String | Integer, fallback : any) : String | float | null
WithDefault counterpart of getSubComponentData. See getDataWithDefault and getSubComponentData.
# evaluateData functions
The sextet of evaluateData* functions is the counterpart to the getData functions. The difference is how the data are treated upon retrieval. While getData functions just return them as value, evaluateData will evaluate them as if they were expressions in the context of the current script. This is useful for storing computations that are different based on the configuration. Special care must be used if data values are strings or expressions. Use single quoted values in the JSON string value to force string data type, e.g.:
{
"data": {
"forcedString": "'single quoted value'", // always a string
"possibleExpression": "expression" // treated as string 'expression' or as value of the variable/parameter called expression.
}
}
However, keep in mind, that getData functions will always include the single quotes.
Function calls are allowed in the evaluated expressions, except any get/evaluateData call in order to prevent cyclic references.
| data entry | getData* result | evaluateData* result |
|---|---|---|
true | 1 | 1 |
"true" | true | 1 |
"'true'" | 'true' as a string | true |
100 | 100 as number | 100 as number |
"100" | 100 as number | 100 as number |
"'100'" | '100' as string | 100 as number |
"100 + 100" | 100 + 100 as string | 200.00 as number |
"'100 + 100'" | '100 + 100' as string | 100 + 100 as string |
"boolParam ? 'yes' : 'no'" | boolParam ? 'yes' : 'no' as string | yes if boolParam is truthy, no if it is falsy |
"someString", no such variable exists | someString as string | someString as string |
"someString", variable exists with a float value 100.00 | someString as string | 100.00 as float |
'someString' | 'someString' | someString |
"some string" | some string as string | some as the first word or value of the variable with the some identifier |
"'some string'" | 'some string' as string | some string as string |
# evaluateData
Same as getData, but considers the value an expression and attempts to evaluate it. See evaluateData functions and getData.
# evaluateDataOrNull
Same as getDataOrNull, but considers the value an expression and attempts to evaluate it. See evaluateData functions and getDataOrNull.
# evaluateDataWithDefault
Same as getDataWithDefault, but considers the value an expression and attempts to evaluate it. See evaluateData functions and getDataWithDefault.
# evaluateSubComponentData
Same as getSubComponentData, but considers the value an expression and attempts to evaluate it. See evaluateData functions and getSubComponentData.
# evaluateSubComponentDataOrNull
Same as getSubComponentDataOrNull, but considers the value an expression and attempts to evaluate it. See evaluateData functions and getSubComponentDataOrNull.
# evaluateSubComponentDataWithDefault
Same as getSubComponentDataWithDefault, but considers the value an expression and attempts to evaluate it. See evaluateData functions and getSubComponentDataWithDefault.
# Available Geometry Functions
The following functions may be only called in geometry, environmentGeometry, previewGeometry and geometryHD scripts.
You can also refer to the scripting course chapter 3D Models & Meshes.
# Instantiation Functions
The following functions instantiate geometry objects.
Note: Some functions have overloads, usually they come either as simple functions or extended functions with UV modifiers and a bevel modifier. You can not use only some modifiers, for example, AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 100, 10}, Vector2f{1, 3});, but rather you have to write the rest of the UV modifier arguments as well, even if their values do not have effect for being neutral to the computation: AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 100, 10}, Vector2f{1, 3}, 0, Vector2f{0, 0});
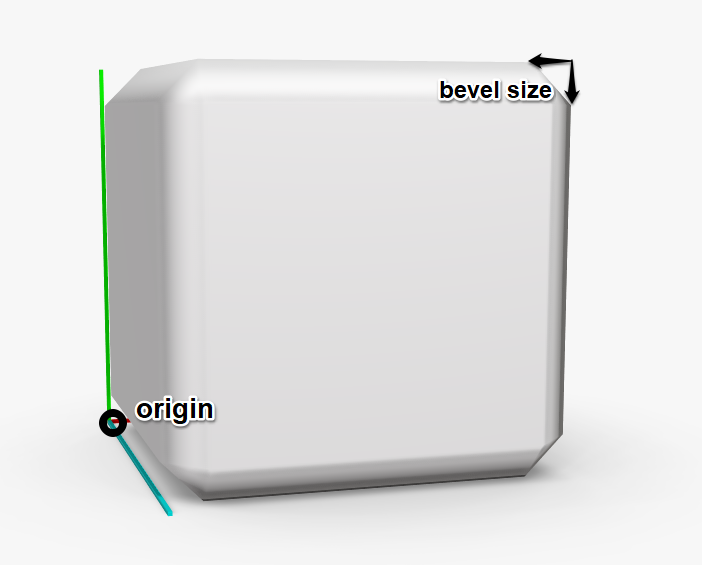
# AddCube
(size: Vector3f) : void
(size: Vector3f, uvScale: Vector2f, uvRotation: float, uvOffset: Vector2f, [bevelSize : float = 2]) : void
Adds a cube of given size to the scene. Cube's origin is in the bottom rear left corner of the cube
Parameters:
sizesize of the cubeuvScalemultiply UV values of the vertices - the higher the value, the smaller the materialuvRotationrotate UV values of the vertices, in a left-hand directionuvOffsetincrease UV values of the vertices -> moves the material in a negative directionbevelSizedefault 2, size of the cube's bevel (measured parallel to its walls)
Usage:
AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000}, Vector2f{1, 1}, 0, Vector2f{0, 0}, 100);
SetObjSurface('isdt:white');
# AddCylinder
(radiusBottom: float, radiusTop: float, height: float, faces: Integer) : void
AddCylinder
(radiusBottom: float, radiusTop: float, height: float, faces: Integer, uvScale: Vector2f, uvRotation: float, uvOffset: Vector2f, [bevelSize : float = 2]) : void
Adds a cylinder or cone (based on if the two radii are same or different). Its origin is in the center of the bottom base.
Parameters:
radiusBottomradius of the bottom baseradiusTopradius of the topheightheight (distance of bottom and top)facesnumber of faces that form the prism approximating the cylinder (3 - triangular prism, 6 - hexagonal prism etc.)uvScalemultiply UV values of the vertices - the higher the value, the smaller the materialuvRotationrotate UV values of the vertices, in a left-hand directionuvOffsetincrease UV values of the vertices -> moves the material in a negative directionbevelSizedefault 2, size of the cube's bevel (measured parallel to its walls)
Usage:
AddCylinder(1000, 300, 2000, 32, Vector2f{1, 1}, 0, Vector2f{0, 0}, 100);
SetObjSurface('isdt:white');

# AddExternalMesh
(meshId: String, boundingBoxSize: Vector3f, boundingBoxOffset: Vector3f) : void
(meshId: String, boundingBoxSize: Vector3f, boundingBoxOffset: Vector3f, uvScale: Vector2f, uvRotation: float, uvOffset: Vector2f) : void
Instantiate a mesh stored in RAPI (the Rubens Admin database). Has an overload for modifying UV settings.
Parameters:
meshIdthe ID of the mesh in acatalogueId:meshNamepatternboundingBoxSizesize of the bounding box of the mesh useful for measurements, camera position and preview cubeboundingBoxOffsetposition of the bounding boxuvScalemultiply UV values of the vertices - the higher the value, the smaller the materialuvRotationrotate UV values of the vertices, in a left-hand directionuvOffsetincrease UV values of the vertices -> moves the material in a negative direction
When performing an export from Blender with the Roomle Blender Addon, you will get a txt file with AddExternalMesh functions accompanying the files you will be uploading to Rubens Admin. You can also get the function from the RuAd mesh entry page.
# AddMesh
(vertices: [Vector3f], indices: [Integer], uvCoordinates [Vector2f], normals[Vector3f]) : void
Creates a mesh from list of vertices and triangles. Overload for UV modifiers is available.
- Parameters:
verticeslist of the verticesindiceslist of indices of the vertices forming the triangles, following a left-hand thumb rule- ⚠️ length of the indices array must be divisible by 3
uvCoordinatesmultiply UV values of the vertices - the higher the value, the smaller the material- ⚠️ length of the array must be the same as the length of the
verticesarray
- ⚠️ length of the array must be the same as the length of the
normalsrotate UV values of the vertices, in a left-hand direction- ⚠️ length of the array must be the same as the length of the
verticesarray
- ⚠️ length of the array must be the same as the length of the
Usage:
n2 = 1 / sqrt(2);
n3 = 1 / sqrt(3);
AddMesh(
Vector3f[
/* 0 */{0, 0, 0},
/* 1 */{300, 0, 0},
/* 2 */{0, 300, 0},
/* 3 */{0, 0, 300}
],
[
0, 1, 2,
0, 3, 1,
0, 2, 3
],
Vector2f[
/* uv coordinate of vertex 0 */{0, 0},
/* uv coordinate of vertex 1 */{600, 0},
/* uv coordinate of vertex 2 */{600, -600},
/* uv coordinate of vertex 3 */{0, 600}
],
Vector3f[
/* normal of vertex 0 */{n3, n3, n3},
/* normal of vertex 1 */{0, n2, n2},
/* normal of vertex 2 */{n2, 0, n2},
/* normal of vertex 3 */{n2, n2, 0}
]
);
SetObjSurface('demoCatalogId:grid');
Creates a mesh from list of vertices, triangles, UV and normal coordinates.
AddMesh
(vertices: [Vector3f]) : void
Creates a mesh from a list of vertices, always creating a triangle between triplet or vertices. UV mapping is automatically computed.
Parameters:
verticeslist of the vertices- ⚠️ length of the vertices array must be divisible by 3
Usage:
AddMesh(
Vector3f[
{0, 0, 0}, {300, 0, 0}, {0, 300, 0}, /* triangle in Z plane */
{0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 300}, {300, 0, 0}, /* triangle in Y plane */
{0, 0, 0}, {0, 300, 0}, {0, 0, 300} /* triangle in X plane */
]
);
SetObjSurface('demoCatalogId:grid');
(vertices: [Vector3f], indices: [Integer]) : void
(vertices: [Vector3f], indices: [Integer], uvScale: Vector2f, uvRotation: float, uvOffset: Vector2f) : void
Creates a mesh from list of vertices and triangles. Overload for UV modifiers is available.
- Parameters:
verticeslist of the verticesindiceslist of indices of the vertices forming the triangles, following a left-hand thumb rule- ⚠️ length of the indices array must be divisible by 3
uvScalemultiply UV values of the vertices - the higher the value, the smaller the materialuvRotationrotate UV values of the vertices, in a left-hand directionuvOffsetincrease UV values of the vertices -> moves the material in a negative direction
Usage:
AddMesh(
Vector3f[
{0, 0, 0}, /* index 0, origin */
{300, 0, 0}, /* index 1, right */
{0, 300, 0}, /* index 2, forward */
{0, 0, 300} /* index 3, top */
],
[
0, 1, 2, /* triangle in Z plane */
0, 3, 1, /* triangle in Y plane */
0, 2, 3 /* triangle in X plane */
]
);
SetObjSurface('demoCatalogId:grid');
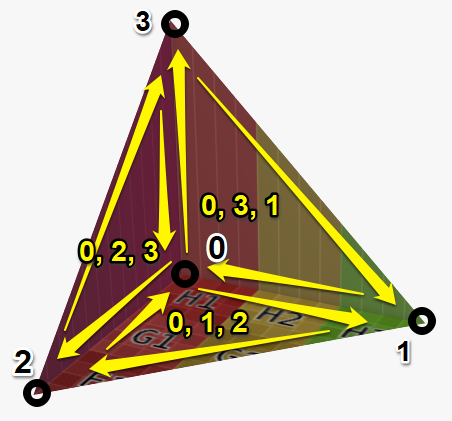
Creates a mesh from list of vertices, triangles, UV and normal coordinates.
# AddPlainCube
(size: Vector3f) : void
A cube with sharp edges. A shortcut for an AddCube with bevel size of 0. Does not have overloads for UVs.
Usage:
AddPlainCube(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
# AddPrism
(extrusionLength: float, vertices: [Vector2f]) : void
AddPrism
(extrusionLength: float, vertices: [Vector2f], uvScale: Vector2f, uvRotation: float, uvOffset: Vector2f, [bevelSize : float = 2]) : void
Extrusion of a planar closed sketch in the Z direction. Bevel is not an actual geometric bevel like in cases of other primitive shapes, but is faked by adjustments of normals.
Parameters:
extrusionLengthlength of the extrusionverticeslist of vertices forming the sketchuvScalemultiply UV values of the vertices - the higher the value, the smaller the materialuvRotationrotate UV values of the vertices, in a left-hand directionuvOffsetincrease UV values of the vertices -> moves the material in a negative directionbevelSizedefault 2, size of the cube's bevel (measured parallel to its walls)
Usage: Example of a 90 degrees slice of a cirle.
/* sine values for angles */
s0 = 0;
s15 = 0.2588190451;
s30 = 0.5;
s45 = 0.7071067812;
s60 = 0.8660254038;
s75 = 0.9659258263;
s90 = 1;
radius = 100;
AddPrism(
100,
Vector2f[
{0, 0},
{radius * s90, radius * s0},
{radius * s75, radius * s15},
{radius * s60, radius * s30},
{radius * s45, radius * s45},
{radius * s30, radius * s60},
{radius * s15, radius * s75},
{radius * s0, radius * s90}
]
);
SetObjSurface('demoCatalogId:grid');

# AddRectangle
(size: Vector2) : void
AddRectangle
(size: Vector2f, uvScale: Vector2f, uvRotation: float, uvOffset: Vector2f) : void
Adds an up facing flat quad in the ground plane with origin in its center.
Parameters:
sizesize of the quaduvScalemultiply UV values of the vertices - the higher the value, the smaller the materialuvRotationrotate UV values of the vertices, in a left-hand directionuvOffsetincrease UV values of the vertices -> moves the material in a negative direction
# AddSphere
(size: Vector3f) : void
AddSphere
(size: Vector3f, uvScale: Vector2f, uvRotation: float, uvOffset: Vector2f) : void
Adds an ellipsoid (sphere if all components are equal). Origin is in the center.
Parameters:
sizesize of the cubeuvScalemultiply UV values of the vertices - the higher the value, the smaller the materialuvRotationrotate UV values of the vertices, in a left-hand directionuvOffsetincrease UV values of the vertices -> moves the material in a negative direction
Usage:
AddSphere(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000}, Vector2f{1, 1}, 0, Vector2f{0, 0});
SetObjSurface('isdt:white');
# Copy
() : void
Adds a copy of the last instantiated object and switches the target of all modifiers to this last instantiated object.
Usage:
screws = 3;
width = 400;
spacing = width / (screws + 1);
offset = spacing / 2;
AddCube(Vector3f{400, 40, 10});
SetObjSurface('isdt:gray');
BeginObjGroup('CREW + NUT + SHIM');
/* shim */
AddCylinder(14, 14, 1, 32, Vector2f{1, 1}, 0, Vector2f{0, 0}, 0);
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{0, 0, -1});
Copy();
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{0, 0, 11});
/* nut */
AddCylinder(10, 10, 7, 6, Vector2f{1, 1}, 0, Vector2f{0, 0}, 0);
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{0, 0, -8});
Copy();
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{0, 0, 19});
/* screw */
AddCylinder(3, 3, 14, 32);
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{0, 0, -2});
EndObjGroup('SCREW + NUT + SHIM');
SetObjSurface('demoCatalogId:chrome');
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{spacing, 20, 0});
/* start with one, we already have the first screw */
for (i = 1; i < screws; i = i + 1) {
Copy();
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{spacing, 0, 0});
}
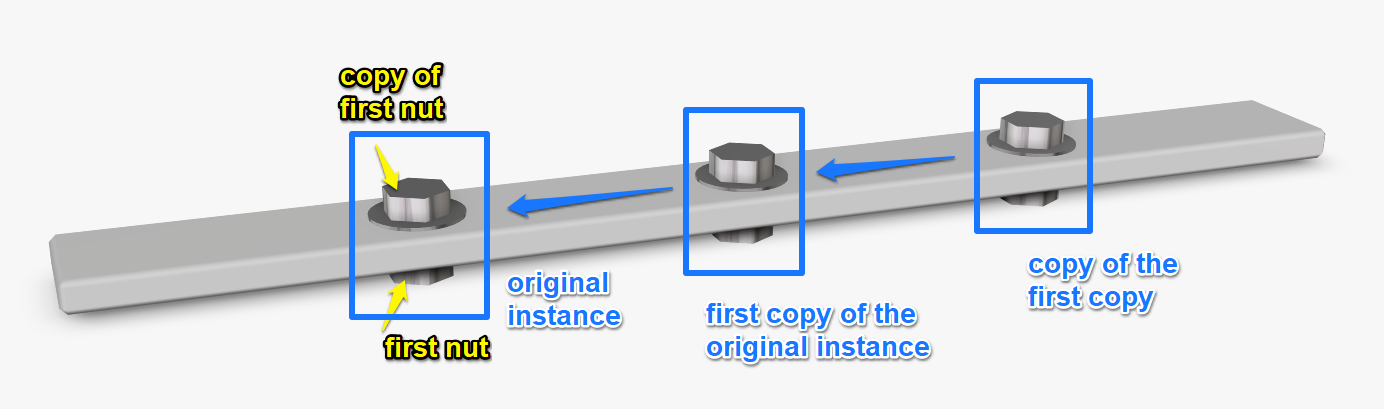
# SubComponent
(subComponentInternalId: String) : void
Instantiates a geometry of the subComponent with its current values. The subComponent must have its active flag set to true. Any modifiers will apply to the whole subComponent geometry as if it was in a group.
For detailed explanation, refer to the SubComponents chapter.
Usage:
"subComponents": [
{
"internalId": "SOFA",
"active": "elementType == 'sofa'",
"numberInPartList": 1,
"assignments": {
"material": "material_primary"
}
}
]
if (elementType == 'SOFA') {
SubComponent('SOFA');
}
# Modifiers
Modifiers are functions called after an object or object group. There are transformations (position, rotation and scale of the object), UV transformations (modify texture mapping) and set material. These functions are indented by an extra space.
Recommended order of transformations (and the most intuitive):
- Scale
- Rotate
- Move
# MoveMatrixBy
(move: Vector3f) : void
Applies translation transformation to the last object or group. The position will be added (not overriden) to any previous transformation.
Parameters:
move: addition to the position vector of the last object or group
Usage:
AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{0, 0, 1000}); /* moves 1000 mm up*/
# RotateMatrixBy
(axis: Vector3f, origin: Vector3f, degrees: float) : void
Applies the rotation transformation to the last object or group around a defined axis by an amount of degrees of angle in a clockwise direction. Hint: This is a left hand rule. If you place your left hand thumb in the direction of the axis, fingers will show the positive direction of the rotation.
Parameters:
axis: a direction vector of the axis around which you rotateorigin: a point definiing the position of the axis (together withaxisdefines the line)degrees: amount of rotation in degrees
Usage:
AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
/* lifts the cube by its left side by 5 degrees */
/* axis goes forward through the lower right side edge */
RotateMatrixBy(Vector3f{0, 1, 0}, Vector3f{1000, 0, 0}, 5);
# ScaleMatrixBy**()(scale: Vector3f, [origin: Vector3f = Vectorf3{0, 0, 0}]) : vo
Applies a scale transform to the last object or group. Neutral value is 1.
Parameters:
scale: amount of scale to apply (multiply to previous, not override)
origin: pivot point of the scaling operation
Usage:
AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
ScaleMatrixBy(Vector3f{1, 1, 0.001}, Vector3f{0, 0, 1000}); /* scales the cube to 1 mm thickness, top surface of the cube stays in place */
# SetObjSurface
(materialId: String) : void
Applies a material from RAPI to the last object or group.
Parameters:
materialId: string in format catalogue:externalId leading to an existing material entry in RAPI
Usage:
AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
SetObjSurface('isdt:black_transparent'); /* applies transparent black material to the cube */
# SetObjSurfaceAttribute
(attributeName: ['color', 'alpha', 'roughness', 'metallic'], attributeValue) : void
Modifies the last object's material shader values. This is especially useful if you intend to have one normal map material which you can afterwards colourize in multiple possible colours.
Parameters:
attributeName: either of'color','alpha','roughness','metallic'string valuesattributeValue:0.0fto1.0fifattributeNameisalpha,rougnessormetallic- if attributeName is color, then a JavaScript compatible color definition, such as:
#ffffffrgb(255, 0, 128)rgb(50%, 0%, 100%)
Usage:
AddSphere(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
SetObjSurface('isdt:red');
SetObjSurfaceAttribute('alpha', 0.5);
SetObjSurfaceAttribute('color', '#00ff00'); // green
# UV Modifiers
Modifiers for UV transforms to modify the mapping of the material. These functions are indented by an extra space.
# MoveUvMatrixBy
(move: Vector2f) : void
Addition to the mesh's UV coordinates. Positive values bring the texture to the left and to down on a cube.
Parameters:
movethe amount to move
Usage:
AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
SetObjSurface('demoCatalogId:grid');
MoveUvMatrixBy(Vector2f{500, 100});
# RotateUvMatrixBy
(degrees: float) : void
Rotation of the mesh's UV coordinates. Positive values rotatet the texture clockwise.
Parameters:
degreesthe amount to rotate
Usage:
AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
SetObjSurface('demoCatalogId:grid');
RotateUvMatrixBy(45);
# ScaleUvMatrixBy
(scale: Vector2f) : void
Multiplication of mesh's UV coordinates. Higher values make the texture smaller. Neutral value is 1.
Parameters:
scalethe amount to scale
Usage:
AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
SetObjSurface('demoCatalogId:grid');
ScaleUvMatrixBy(Vector2f{2, 1});
# SetUvTransform
(uvScale: Vector2f, uvRotation: float, uvOffset: Vector2f : void
Sets the UV trasnforms to a given values. This overrides any previous modifiers.
Parameters:
uvScalemultiply UV values of the vertices, neutral value is 1uvRotationrotate UV values of the vertices, in a left-hand directionuvOffsetincrease UV values of the vertices
# Grouping Functions
# BeginObjGroup
() : void
Starts an object group. All further geometry objects until the EndObjGroup(); call will be in the same group and will be affected by all other modifiers at once.
BeginObjGroup(); will indent furher code by 4 spaces. Every BeginObjGroup(); must match to an EndObjGroup();. Can be nested in any way and combined with SubComponent or CSG operator calls.
Parameters:
- there are no arguments, but it is a common to pass a String argument defining the name of the group, however this serves more like as a comment and is ignored by the core.
Usage:
BeginObjGroup();
AddCube(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
SetObjSurface('isdt:blue');
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{ -1000, 0, 0});
AddSphere(Vector3f{1000, 1000, 1000});
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{0, 0, 500});
SetObjSurface('isdt:green');
EndObjGroup();
SetObjSurface('isdt:red'); /* overrides colour of the objects in the group, all will be red */
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{0, 500, 0});
/*
adds to the position of the objects in the group:
* cube is at {-1000, 500, 0}
* sphere is at {0, 500, 500}
*/
# EndObjGroup
() : void
Closes the group started by BeginObjGroup. Removes 4 spaces from indentation.
# CSG Boolean Operators
These functions provide boolean operation on meshes. You can for example subtract a cylinder from a cube, making a hole through the cube.
⚠️ Those operators are expensive and should not be used unless a different approach can be utilized. They work best with primitives, the performance on meshes is not good.
# AndOperator
() : void
Interserction of the last two objects or meshes.
Usage:
AddSphere(Vector3f{500, 500, 500});
AddCube(Vector3f{400, 400, 400}, Vector2f{5, 5}, 0, Vector2f{0, 0}, 0);
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{ -400 / 2, -400 / 2, -400 / 2});
AndOperator();

# MinusOperator
() : void
Subtracts the geometry of the last object from the penultimate object. Intersection plane will have imprinted the last object's UV map values.
Usage:
AddSphere(Vector3f{500, 500, 500});
AddCube(Vector3f{400, 400, 400}, Vector2f{5, 5}, 0, Vector2f{0, 0}, 0);
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{ -400 / 2, -400 / 2, -400 / 2});
MinusOperator();

# OrOperator
() : void
Union of two last geometry objects. Works similarily to an object group, but bakes the meshes in one, removing vertices inside the internal volume.
Usage:
AddSphere(Vector3f{500, 500, 500});
AddCube(Vector3f{400, 400, 400}, Vector2f{5, 5}, 0, Vector2f{0, 0}, 0);
MoveMatrixBy(Vector3f{ -400 / 2, -400 / 2, -400 / 2});
MinusOperator();

# Miscellaneous
# hasEqualGeometry
# Tools and Importer Meta Keywords
The following features are ignored by the Roomle Rubens Configurator core, but provide different functionalities in other development tools and importers.
# TODO
A comment starting with TODO will appear in the VS Code Outline. This is a function provided by the VS Code extension and roomle-content-tool-api
Usage:
// TODO add check for validity
# FIXME
A comment starting with FIXME will appear in the VS Code Outline. This is a function provided by the VS Code extension and roomle-content-tool-api
Usage:
/* FIXME gap if size > 200 */
# #tag
This is used by the Roomle Component Tool extension for Visual Studio Code. This must be commented out, because it is unknown to the Roomle Core.
Defines a tag that will show in the Outline pane.
Usage:
"onUpdate": "
...
#tag THIS WILL APPEAR IN THE CODE OUTLINE
...
"
"parentDockings": {
"points": [
{
"mask": "
#tag Top Left Connector
'connector'
",
"position": "{-width / 2, 0, height}"
}
]
}
# #region and #endregion
This is used by the Roomle Component Tool extension for Visual Studio Code. This must be commented out, because it is unknown to the Roomle Core.
Defines a tag that will show in the Outline pane. Defines a code folding region for organizing code and displays the #region in the Outline pane in the same way as a tag
Usage:
#region Docking variables
if (elementType == 'straight_left_armrest') {
leftDock_allowed = false;
rightDock_allowed = true;
rightDock_position = Vector3f{520, 0, 0};
...
}
...
#endregion
# BEGIN CUSTOM CODE and END CUSTOM CODE
This is used by the IDM importer.
Commented out in the onUpdate script, provides an importer directive to keep the code in between those markers.
Usage:
/* BEGIN CUSTOM CODE */
/* This code will remain after a reimport into this catalogue. */
if (isnull(inited)) {
inited = true;
myCustomVariable = 'some value';
}
myCustomVar_isLeather = idmFeature2 == 'LE';
/* END CUSTOM CODE */
